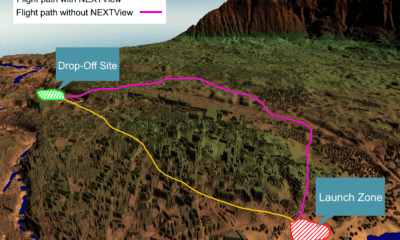
Drone Hive
Drones for Mine Surveying
Miners are increasingly depending on drones to do their survey work.
What does a mine survey entail?
A mine survey involves measuring and mapping the mining area on or below the surface of earth at all stages of the mining process – from prospecting to utilisation of mineral deposits.
Play
Surveys are performed to:
- assess risk and environmental impact on surrounding areas to determine the viability of a site
- determine the location, dimensions and characteristics of the mineral deposits, adjoining rocks and the surface
- estimate the mineral availability, extraction and production potential and the valuation of the mineral deposits, to determine the viability and profitability of the mine.
These form the basis for planning and control of mine workings, and are essential for efficient and safe operations. Regular surveys in ongoing mining operations study rock and ground movements due to mining operations and are used to forecast future movements, allowing miners to take necessary precautions and remedial measures.
Play
The entry of drones
Mining surveillance, monitoring and supervision are typically capital and labor intensive. Mining operators across the globe have been testing drones since 2014. More recently, small sized drones have aided firms in exploration for mineral deposits and mapping mineral deposit sites. They can also be used to calculate inventory and monitor stockpiles, using relevant sensors and data tools.
Play
Drones in exploration
Often mining properties are located in remote areas that are either unmapped or have maps of poor resolution. This forces prospectors or potential miners to conduct an early stage exploration of the area. Previously this required conventional aerial photography, which can be cost prohibitive.
The advent of drones has changed the equation somewhat. Drones can conduct a high resolution mapping of an extensive area in a few hours and at a fraction of the cost of conventional mapping. Technological advancements have enabled the use of small high resolution sensors, miniature GPS and computer boards in drones, leading to lower overall operational cost, without compromising on the quality of mapping required.
Some advantages of using drones over conventional mapping are:
- Significantly lower cost (conventional mapping cost could be up to 10x the cost of mapping using drones)
- Drones capture high resolution image even with a 16mp camera as they fly close to the ground (at 250 ft). On the other hand, a conventional aerial survey requires cameras with much higher resolution (> 80mp) to deliver comparable quality data because of their required elevation of 2000-5000 ft. Other alternatives such as satellite imagery provide much weaker output and cost is also prohibitive.
- Drones can create topographical maps and GIS data in remote areas, whereas previously mapping required ground surveyors to walk across the entire property with an RTK/GPS rover to collect GPS points for mapping.
- Low cost of data allows close-up 3D view of the properties at an early exploration stage, aiding in project planning.
Technology highlights
Remote sensing has significant applications in prospecting. Infrared, hyper/multispectral cameras and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging – a remote sensing survey method using pulsed laser light to measure distance) is aiding in adopting existing satellite based techniques to map underground areas and identify mineral deposits.
Different ore bodies have different electromagnetic spectral signatures. Multi-spectral imagery is used to detect such ore deposits through computer processing of images taken by drones.
Drones can conduct long range aerial magnetometer surveys. High resolution aeromagnetic maps reflect the underlying geology of an area, helping interpret various structures and rock type distributions. In case of open pit mines, having an accurate terrain model becomes critical to know how much material is being moved on a day-to-day basis. Terrain models are also helpful to explore areas before and after mines are built.
Aerial photogrammetry is used to create topographical maps. Aerial photogrammetry combines aerial photography shots to create primarily 3D models. Multiple aerial shots from at least two different angles, and sometimes other technologies like laser scanners, white light digitizers and LiDAR are combined to create a detailed output.
Play
Conclusion
Drones add significant value to every part of the mining life cycle. Drones simplify the collection and analysis of data, allowing professionals in mine surveying to make better decisions, faster.